Line Set¶
Overview¶
A line set is essentially just a set of tubes of a reasonably long length that allows for fluid to be moved from one place to another. It is commonly insulated in order to decrease heat transfer between the tube and ambient.
Mathematical Description¶
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
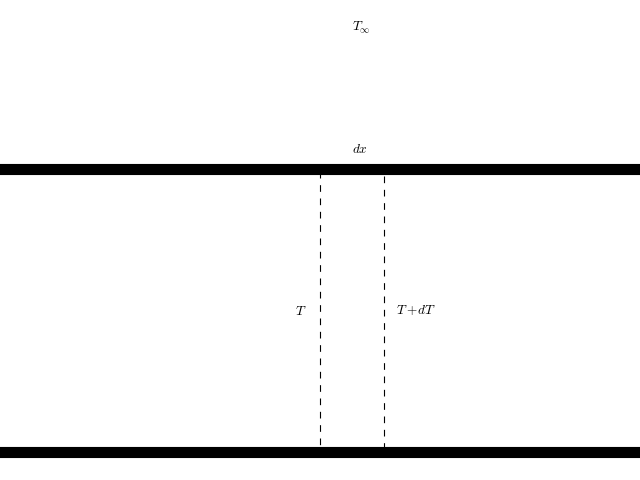
An energy balance over the control volume in the tube gives
(1)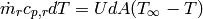
where if 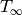 is greater than
is greater than 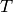 , the differential
, the differential 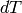 is positive. Therefore separation of variables yields
is positive. Therefore separation of variables yields
(2)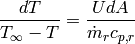
and upon integration (with a 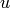 -substitution)
-substitution)
(3)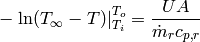
finally yields
(4)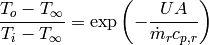
and the outlet temperature from
(5)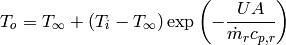
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
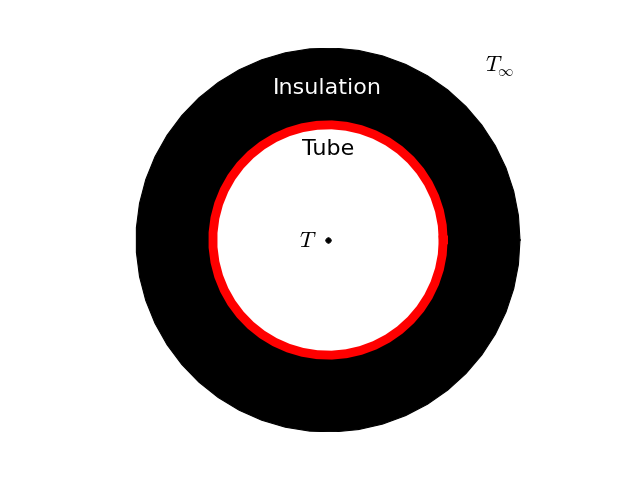
Based on the concentric geometry, the heat transfer network terms are given by
(6)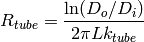
(7)![R_{insul}=\frac{\ln[(D_o+2t_{insul})/D_o]}{2\pi L k_{insul}}](../_images/math/aab89e37b301fc547f4dc38b84594fccbfbbb30c.png)
(8)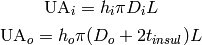
and the overall heat conductance is given by
(9)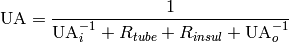
The pressure drop and refrigerant charge are evaluated from section Single-phase refrigerant pressure drop, heat transfer and charge.
Nomenclature
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
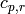 |
Refrigerant specific heat [J/kg/K] |
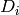 |
Inner diameter of tube [m] |
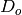 |
Outer diameter of tube [m] |
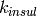 |
Thermal conductivity of insulation [W/m/K] |
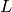 |
Length of tube [m] |
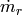 |
Refrigerant mass flow rate [kg/s] |
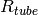 |
Thermal resistance from tube [K/W] |
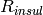 |
Thermal resistance from insulation [K/W] |
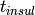 |
Thickness of insulation [m] |
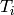 |
Inlet temperature [K] |
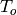 |
Outlet temperature [K] |
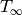 |
Ambient temperature [K] |
 |
Overall heat transfer conductance [W/K] |
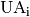 |
Inner heat transfer conductance [W/K] |
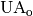 |
Outer heat transfer conductance [W/K] |
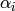 |
Inner heat transfer coefficient [W/m2/K] |
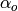 |
Outer heat transfer coefficient [W/m2/K] |